Статистика
Онлайн всего: 1 Гостей: 1 Пользователей: 0
|
Топики
В категории материалов: 4
Показано материалов: 1-4 |
|
Сортировать по:
Дате ·
Названию ·
Рейтингу ·
Комментариям ·
Просмотрам
"Lymphatic drainage" redirects here. For the massage technique, see Manual lymphatic drainage. Lymphatic System Human lymphatic system Latin systema lymphoideum The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system, comprising a network of conduits called lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph (from Latin lympha "water goddess"[1]) unidirectionally towards the heart. The lymphatic system was first described in the seventeenth century independently by Olaus Rudbeck and Thomas Bartholin. The lymph system is not a closed system. The circulatory system processes an average of 20 liters of blood per day through capillary filtration which removes plasma while leaving the blood cells. Roughly 17 liters of the filtered plasma actually get reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining 3 liters are left behind in the interstitial fluid. The primary function of the lymph system is to provide an accessory route for these excess 3 liters per day to get returned to the blood.[2] Lymph is essentially recycled blood plasma. Lymphatic organs play an important part in the immune system, having a considerable overlap with the lymphoid system. Lymphoid tissue is found in many organs, particularly the lymph nodes, and in the lymphoid follicles associated with the digestive system such as the tonsils. Lymphoid tissues contain lymphocytes, but they also contain other types of cells for support.[3] The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and production of lymphocytes (the primary cellular component of lymph), which includes the spleen, thymus, bone marrow, and the lymphoid tissue associated with the digestive system. |
 Tissues TissuesA tissue is a group of cells specialized for a common purpose. Tissues are composed of cells and interstitial fluid involved in material exchange with the environment. An animal has four main tissues. Animal tissues |
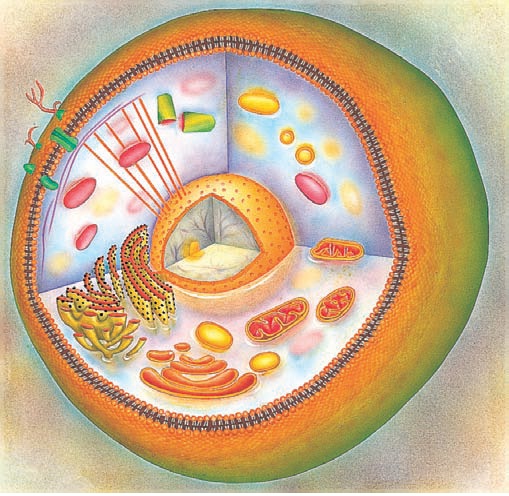
Cells are the building blocks of all living things, either unicellular or multicellular. All metabolic activities are performed within cells. Metabolism, excretion, reproduction, respiration, irritability and growth are the basic functions that cells must perform. Cells have vital roles in the survival of an organism despite their differences in structure and function. All are involved in different functions such as movement, |
BODY ORGANIZATION OF ORGANISMS Organisms develop from a zygote formed by the fertilization of an egg by a sperm. A living organism can carry out all its biological functions, survive independently, grow and develop during its life span and reproduce to form offspring. An organism includes six groups of components (in order of size): atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs and systems. These components are closely related to each other for the survival of the organism. Anatomy deals with the structures that constitute the organism, while physiology deals with the function of these structures. |
|
|
| | |
 Tissues
Tissues